Introduction
Deep learning has improved the performance of neural network architectures such as recurrent neural networks (RNN and LSTM) and convolutional neural networks (CNN) in tackling a variety of Natural Language Processing (NLP) problems such as text categorisation, language modelling, machine translation, and so on. Transfer learning is a method of using a deep learning model that has been trained on a big dataset to perform similar tasks on a new dataset. A deep learning model like this is referred to as a pre-trained model. As a result, the demand for NLP transfer learning was at an all-time high. In the paper “Attention is All You Need,” published in 2018, Google unveiled the transformer, which proved to be a watershed moment in NLP.
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) is an acronym for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. It is intended to condition both left and right context to pre-train deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text. As a result, using just one additional output layer, the pre-trained BERT model may be fine-tuned to generate state-of-the-art models for a wide range of NLP tasks.
Data
In this article, the Consumer Complaint Database is used, which is a collection of complaints about consumer financial products and services that we sent to companies for response.
Load Package
import re
import math
import torch
import warnings
import torch.nn as nn
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pytorch_lightning as pl
import torch.nn.functional as F
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn import metrics
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from transformers import BertModel, AdamW
from tqdm import tqdm
from pytorch_lightning.metrics import functional as FM
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")Text Preprocessing
I made this dataset into a triple-class classification problem.
def clean_text(text):
REPLACE_BY_SPACE_RE = re.compile('[/(){}\[\]\|@,;]')
BAD_SYMBOLS_RE = re.compile('[^0-9a-z #+_]')
text = text.lower()
text = REPLACE_BY_SPACE_RE.sub(' ', text)
text = BAD_SYMBOLS_RE.sub('', text)
text = text.replace('x', '')
text = text.strip()
return text
df = pd.read_csv(r"C:\Users\Yang\Desktop\Dissertation\data\test\complaints.csv")
df = df[(df["label"]=="Money transfers") | (df["label"]=="Prepaid card") | (df["label"]=="Payday loan")]
df = df[["Consumer complaint narrative", "Product"]]
df.columns = ["text", "label"]
df = df.dropna()
df = df.reset_index(drop=True)
df["text"] = df["text"].map(str)
df["text"] = df["text"].apply(clean_text)Transform Text into IDs
We will try to encode a couple of sentences using the tokeniser.
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
input_ids = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(df["text"].tolist(),
padding=True,
truncation=True,
max_length=128,
add_special_tokens=True,
return_tensors="pt",
return_token_type_ids=False,
return_attention_mask=False)Encode the Label
le = LabelEncoder()
y = le.fit_transform(df["label"])
classes = le.classes_Separate the Data
X_train, X_valid, y_train, y_valid = train_test_split(input_ids["input_ids"].numpy(),
y,
test_size=0.3,
random_state=914,
stratify=y)
X_valid, X_test, y_valid, y_test = train_test_split(X_valid,
y_valid,
test_size=0.5,
random_state=914,
stratify=y_valid)Build Dataset and Dataloader
class TextDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, input_ids, labels):
self.X = input_ids
self.y = labels
def __len__(self):
return len(self.y)
def __str__(self):
return f"<Dataset(N={len(self)})>"
def __getitem__(self, index):
X = self.X[index]
y = self.y[index]
X = torch.tensor(X, dtype=torch.long)
y = torch.tensor(y, dtype=torch.long)
return [X, y]
def create_dataloader(self, batch_size, shuffle=False, drop_last=False, num_workers=0):
return torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset=self,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=shuffle,
drop_last=drop_last,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=num_workers)train_dataset = TextDataset(X_train, y_train)
valid_dataset = TextDataset(X_valid, y_valid)
test_dataset = TextDataset(X_test, y_test)
batch_size = 16
train_dataloader = train_dataset.create_dataloader(batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=0)
valid_dataloader = valid_dataset.create_dataloader(batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=0)
test_dataloader = test_dataset.create_dataloader(batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=0)Modelling
In this article, I will only contruct four text classification models, namely TextCNN, LSTM, XVectors, and BERT. Build a pl.LightningModule class for future use.
class MultiClass(pl.LightningModule):
"""
Multi-class Classification
"""
def __init__(self, learning_rate=1e-3):
super().__init__()
# Set our learning rate
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
# Create loss function
self.loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
self.train_losses = []
self.valid_losses = []
self.train_accuracies = []
self.valid_accuracies = []
def configure_optimizers(self):
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate)
return optimizer
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
batch, y = batch
y_hat = self(batch)
labels_hat = torch.argmax(y_hat, dim=1)
n_correct_pred = torch.sum(y == labels_hat).item()
loss = F.cross_entropy(y_hat, y.long())
tensorboard_logs = {'train_acc_step': n_correct_pred, 'train_loss_step': loss}
return {'loss': loss, "n_correct_pred": n_correct_pred, "n_pred": len(y), 'log': tensorboard_logs}
def training_epoch_end(self, outputs):
avg_loss = torch.stack([x['loss'] for x in outputs]).mean()
train_acc = sum([x['n_correct_pred'] for x in outputs]) / sum(x['n_pred'] for x in outputs)
tensorboard_logs = {'train_acc': train_acc, 'train_loss': avg_loss, 'step': self.current_epoch}
self.train_losses.append(avg_loss.detach().cpu().item())
self.train_accuracies.append(train_acc)
# return {'loss': avg_loss, 'log': tensorboard_logs}
def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
batch, y = batch
y_hat = self(batch)
loss = F.cross_entropy(y_hat, y.long())
labels_hat = torch.argmax(y_hat, dim=1)
n_correct_pred = torch.sum(y == labels_hat).item()
return {'val_loss': loss, "n_correct_pred": n_correct_pred, "n_pred": len(y)}
def validation_epoch_end(self, outputs):
avg_loss = torch.stack([x['val_loss'] for x in outputs]).mean()
val_acc = sum([x['n_correct_pred'] for x in outputs]) / sum(x['n_pred'] for x in outputs)
tensorboard_logs = {'val_loss': avg_loss, 'val_acc': val_acc, 'step': self.current_epoch}
self.valid_losses.append(avg_loss.detach().cpu().item())
self.valid_accuracies.append(val_acc)
return {'log': tensorboard_logs}
def test_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
batch, y = batch
y_hat = self(batch)
loss = F.cross_entropy(y_hat, y.long())
labels_hat = torch.argmax(y_hat, dim=1)
n_correct_pred = torch.sum(y == labels_hat).item()
return {'test_loss': loss, "n_correct_pred": n_correct_pred, "n_pred": len(y)}
def test_epoch_end(self, outputs):
avg_loss = torch.stack([x['test_loss'] for x in outputs]).mean()
test_acc = sum([x['n_correct_pred'] for x in outputs]) / sum(x['n_pred'] for x in outputs)
tensorboard_logs = {'test_loss': avg_loss, 'test_acc': test_acc, 'step': self.current_epoch}
return {'log': tensorboard_logs}
def predict(self, test_dataloader):
"""Prediction step."""
# Set model to eval mode
self.eval()
y_probs = []
# Iterate over val batches
with torch.no_grad():
for i, batch in enumerate(test_dataloader):
x, y = batch
x, y = x.to(self.device), y.to(self.device)
# Forward pass with inputs
y_prob = self(x)
# Store outputs
y_probs.extend(y_prob.cpu())
return self.softmax(np.vstack(y_probs))
def softmax(self, x):
"""Compute softmax values for each sets of scores in x."""
exp_ = np.exp(x - np.max(x))
return exp_ / exp_.sum(axis=0)A function to initialise the weights and biases.
def init_weights(m):
for name, param in m.named_parameters():
nn.init.normal_(param.data, mean=0, std=0.1)TextCNN
The convolutional neural network for text, or TextCNN, is a helpful deep learning technique for tasks including sentiment analysis and question classification.
class TextCNN(MultiClass):
"""
https://finisky.github.io/2020/07/03/textcnnmvp/
"""
def __init__(self, embed_num, embed_dim, class_num, kernel_num=100, kernel_sizes=[3, 4, 5], dropout=0.5):
super(TextCNN, self).__init__()
Ci = 1
Co = kernel_num
self.embed = nn.Embedding(embed_num, embed_dim)
self.convs = nn.ModuleList([nn.Conv2d(Ci, Co, (f, embed_dim), padding=(2, 0)) for f in kernel_sizes])
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.fc = nn.Linear(Co * len(kernel_sizes), class_num)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.embed(x) # (N, token_num, embed_dim)
x = x.unsqueeze(1) # (N, Ci, token_num, embed_dim)
x = [F.relu(conv(x)).squeeze(3) for conv in self.convs] # [(N, Co, token_num) * len(kernel_sizes)]
x = [F.max_pool1d(i, i.size(2)).squeeze(2) for i in x] # [(N, Co) * len(kernel_sizes)]
x = torch.cat(x, 1) # (N, Co * len(kernel_sizes))
x = self.dropout(x) # (N, Co * len(kernel_sizes))
logit = self.fc(x) # (N, class_num)
return logitStart training.
textcnn = TextCNN(len(tokenizer.vocab), 300, 3, 100, [3, 4, 5], 0.1)
trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=1, fast_dev_run=False, max_epochs=10)
trainer.fit(textcnn, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader)
test_probs = textcnn.predict(test_dataloader)
test_preds = np.argmax(test_probs, axis=1)Visualise the accuracy and loss.
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(textcnn.train_accuracies)), textcnn.train_accuracies, label="train")
plt.plot(range(len(textcnn.valid_accuracies)), textcnn.valid_accuracies, label="valid")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()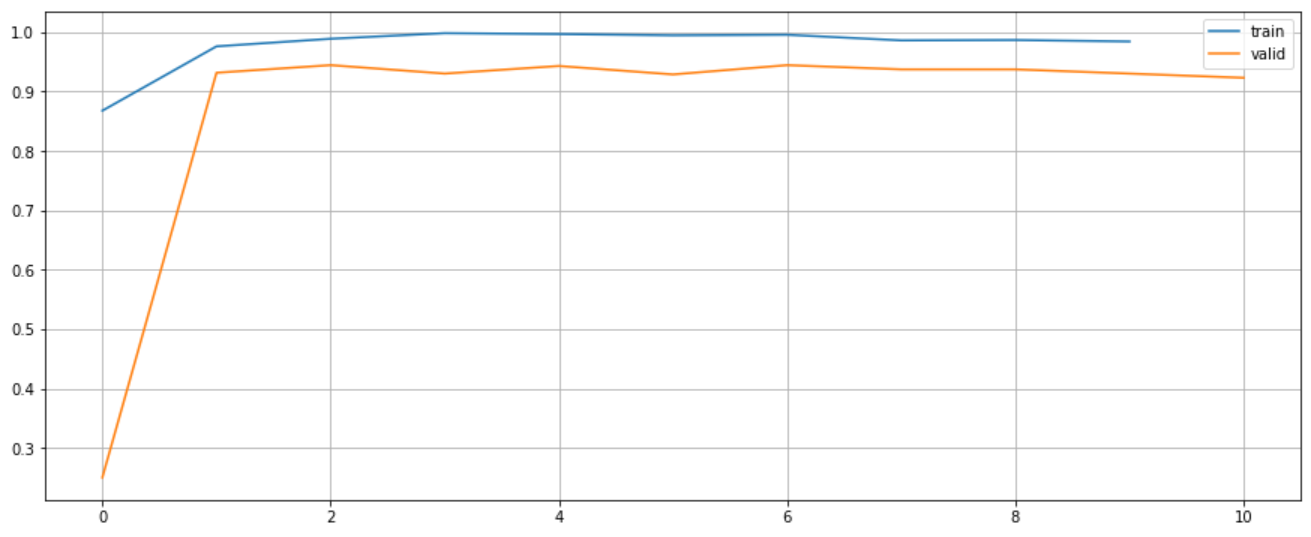
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(textcnn.train_losses)), textcnn.train_losses, label="train")
plt.plot(range(len(textcnn.valid_losses)), textcnn.valid_losses, label="valid")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()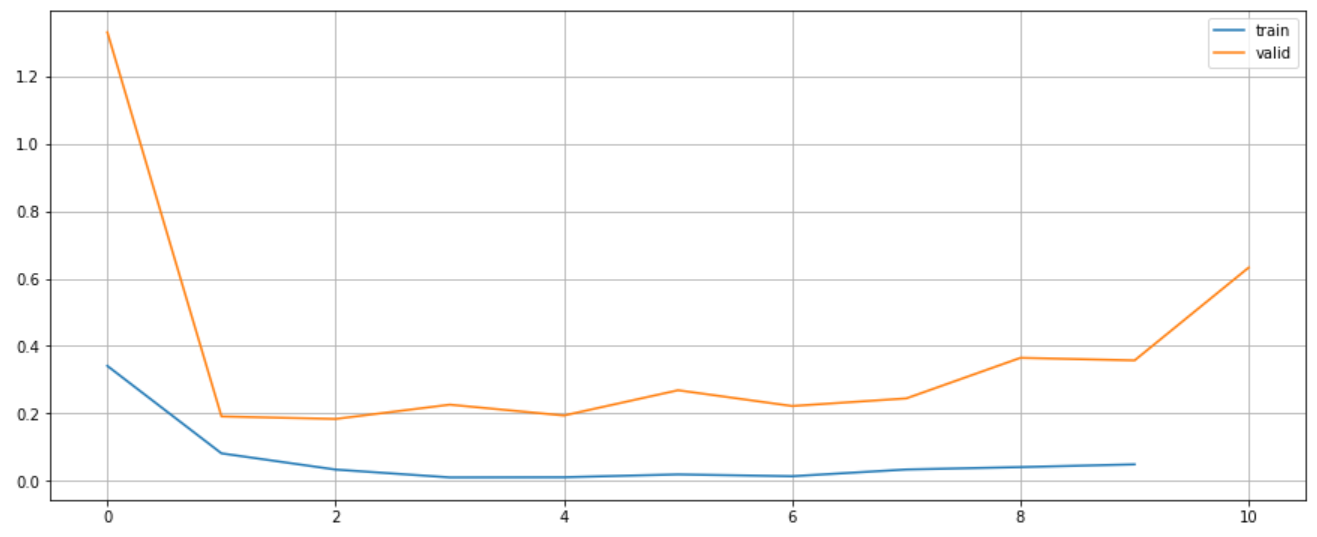
Confusion matrix.
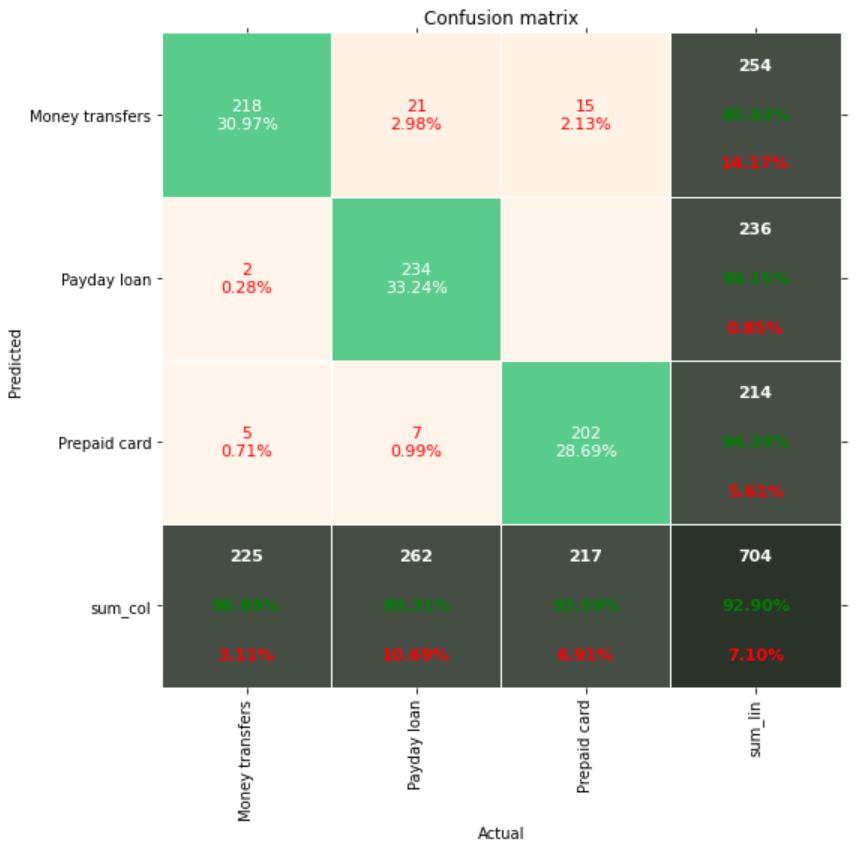
XVectors
Variable-length utterances are mapped to fixed-dimensional embeddings called x-vectors by the DNN, which has been trained to discriminate between speakers. In this article, I tried using it to classify text.
class StatsPool(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, floor=1e-10, bessel=False):
super(StatsPool, self).__init__()
self.floor = floor
self.bessel = bessel
def forward(self, x):
means = torch.mean(x, dim=1)
_, t, _ = x.shape
if self.bessel:
t = t - 1
residuals = x - means.unsqueeze(1)
numerator = torch.sum(residuals**2, dim=1)
stds = torch.sqrt(torch.clamp(numerator, min=self.floor)/t)
x = torch.cat([means, stds], dim=1)
return x
class TDNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
input_dim=23,
output_dim=512,
context_size=5,
stride=1,
dilation=1,
batch_norm=True,
dropout_p=0.0,
padding=0
):
super(TDNN, self).__init__()
self.context_size = context_size
self.stride = stride
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.dilation = dilation
self.dropout_p = dropout_p
self.padding = padding
self.kernel = nn.Conv1d(self.input_dim,
self.output_dim,
self.context_size,
stride=self.stride,
padding=self.padding,
dilation=self.dilation)
self.nonlinearity = nn.ReLU()
self.batch_norm = batch_norm
if batch_norm:
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(output_dim)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(p=self.dropout_p)
def forward(self, x):
'''
input: size (batch, seq_len, input_features)
outpu: size (batch, new_seq_len, output_features)
'''
_, _, d = x.shape
assert (d == self.input_dim), 'Input dimension was wrong. Expected ({}), got ({})'.format(
self.input_dim, d)
x = self.kernel(x.transpose(1, 2))
x = self.nonlinearity(x)
x = self.drop(x)
if self.batch_norm:
x = self.bn(x)
return x.transpose(1, 2)
class XVectors(MultiClass):
def __init__(
self,
embed_num,
embed_dim,
class_num,
dropout_p=0.0
):
super(XVectors, self).__init__()
self.embed = nn.Embedding(embed_num, embed_dim)
self.tdnn1 = TDNN(input_dim=embed_dim, output_dim=512, context_size=3, padding=math.floor(3/2))
self.tdnn2 = TDNN(input_dim=512, output_dim=512, context_size=1, padding=math.floor(1/2))
self.tdnn3 = TDNN(input_dim=512, output_dim=1500, context_size=1, padding=math.floor(1/2))
self.tdnnres1 = TDNN(input_dim=512, context_size=5, padding=math.floor(5/2))
self.tdnnres2 = TDNN(input_dim=512, context_size=5, padding=math.floor(5/2))
self.tdnnres3 = TDNN(input_dim=512, context_size=1, padding=math.floor(1/2))
self.pool = StatsPool()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(3000, 512)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 512)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p)
self.nonlinearity = nn.ReLU()
self.classifier = nn.Linear(512, class_num)
def forward(self, x):
# Residual TDNN based Frame-level Feature Extractor
x = self.embed(x)
x = self.tdnn1(x)
x = self.tdnn2(x)
x = self.tdnnres1(x) + x
x = self.tdnnres2(x) + x
x = self.tdnnres3(x) + x
x = self.tdnn3(x)
# Statistics Pooling
x = self.pool(x)
# DNN based Segment level Feature Extractor
x = self.linear1(x)
x = self.nonlinearity(self.dropout1(self.bn1(x)))
x = self.linear2(x)
x = self.nonlinearity(self.dropout2(self.bn2(x)))
# Classifier
x = self.classifier(x)
return xStart training.
xvectors = XVectors(len(tokenizer.vocab), 300, 3)
trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=1, fast_dev_run=False, max_epochs=20)
trainer.fit(xvectors, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader)
test_probs = xvectors.predict(test_dataloader)
test_preds = np.argmax(test_probs, axis=1)Visualise the accuracy and loss.
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(xvectors.train_accuracies)), xvectors.train_accuracies, label="train")
plt.plot(range(len(xvectors.valid_accuracies)), xvectors.valid_accuracies, label="valid")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()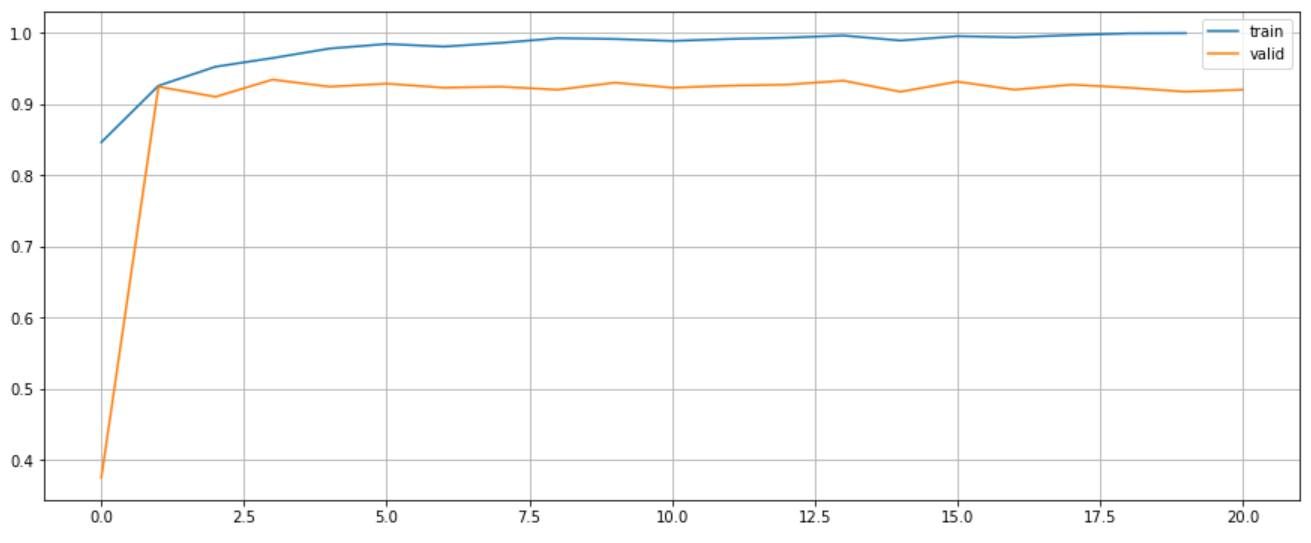
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(xvectors.train_losses)), xvectors.train_losses, label="train")
plt.plot(range(len(xvectors.valid_losses)), xvectors.valid_losses, label="valid")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()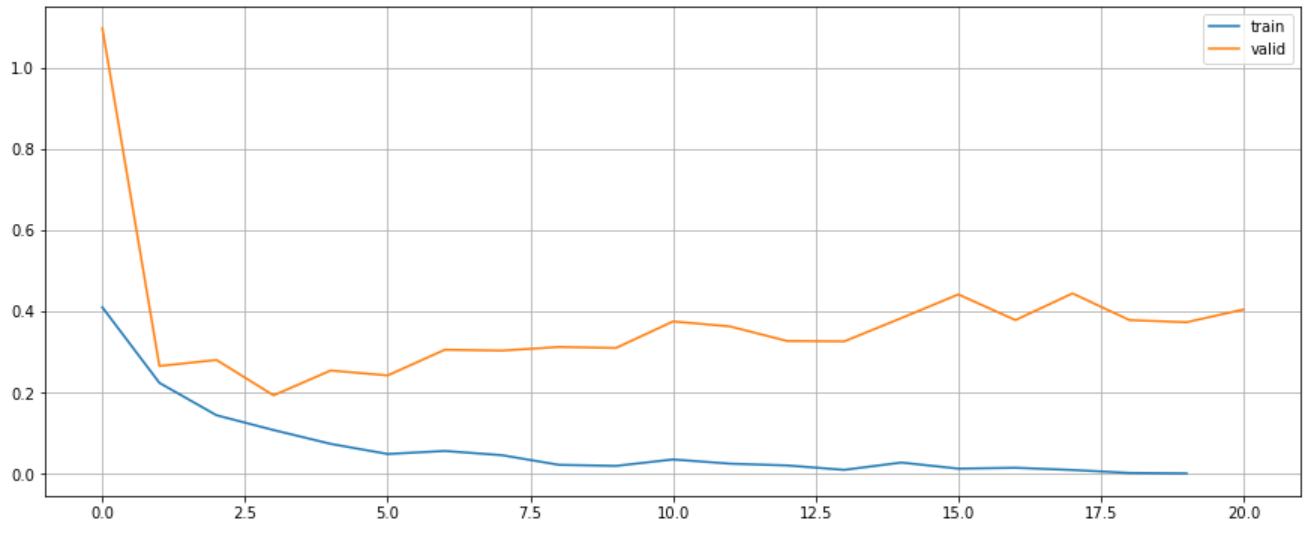
Confusion matrix.
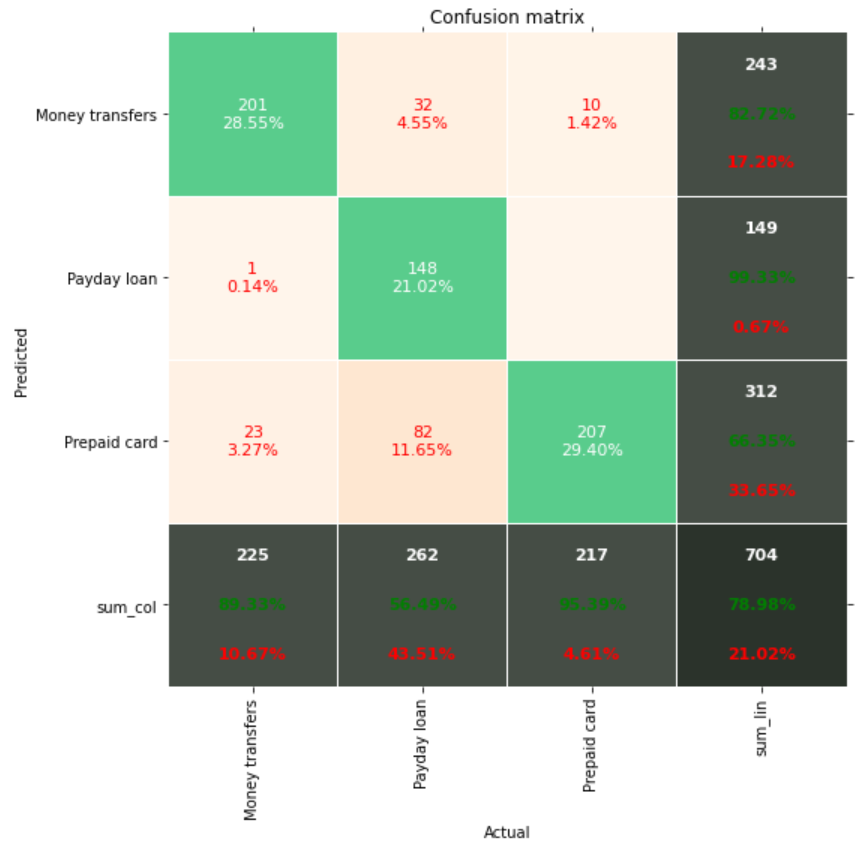
LSTM
Just like RNN, LSTM has a sequential model. The difference between RNN and LSTM is that it has additional signal information that is given from one time step to the next time step which is commonly called “cell memory.” LSTM is designed to overcome the problem of vanishing gradient, using the gate mechanism.
class SimpleLSTM(MultiClass):
def __init__(self, embed_num, embed_dim, hidden_size, class_num):
super(SimpleLSTM, self).__init__()
self.embed = nn.Embedding(embed_num, embed_dim)
self.lstm1 = nn.LSTM(input_size=embed_dim, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=1, batch_first=True)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(hidden_size, class_num)
def forward(self, x):
# x's shape must be (batch, seq_len, input_size)
x = self.embed(x)
_, (h, _) = self.lstm1(x)
x = self.classifier(h.view(h.shape[1], h.shape[2]))
return xStart training.
lstm = SimpleLSTM(len(tokenizer.vocab), 300, 64, 3)
trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=1, fast_dev_run=False, max_epochs=20)
trainer.fit(lstm, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader)
test_probs = lstm.predict(test_dataloader)
test_preds = np.argmax(test_probs, axis=1)Visualise the accuracy and loss.
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(lstm.train_accuracies)), lstm.train_accuracies, label="train")
plt.plot(range(len(lstm.valid_accuracies)), lstm.valid_accuracies, label="valid")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()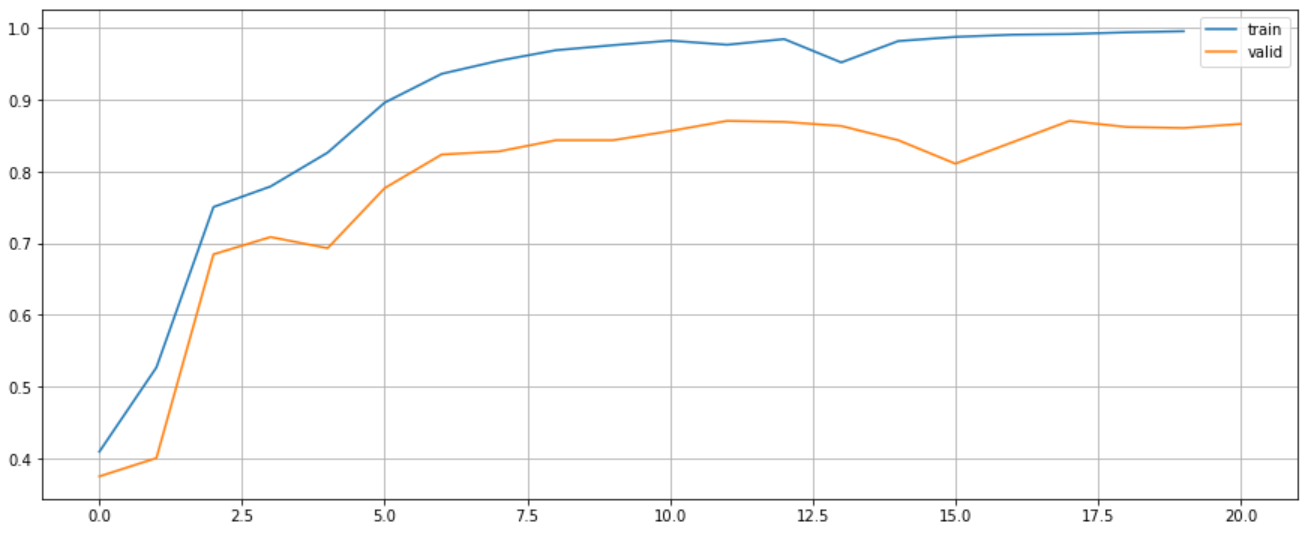
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(lstm.train_losses)), lstm.train_losses, label="train")
plt.plot(range(len(lstm.valid_losses)), lstm.valid_losses, label="valid")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()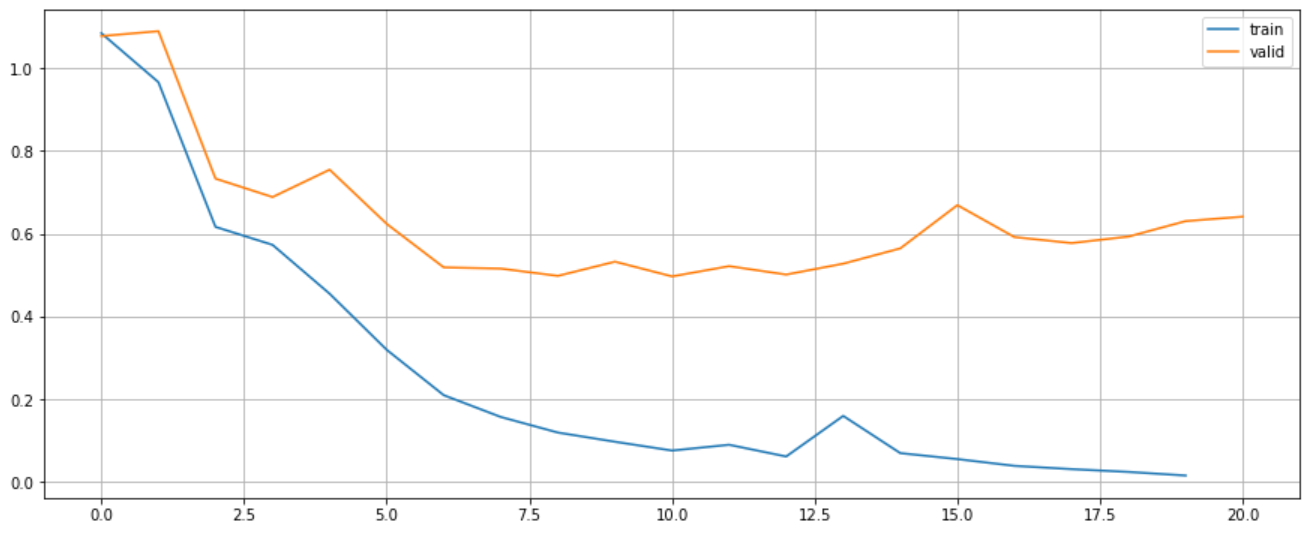
Confusion matrix.
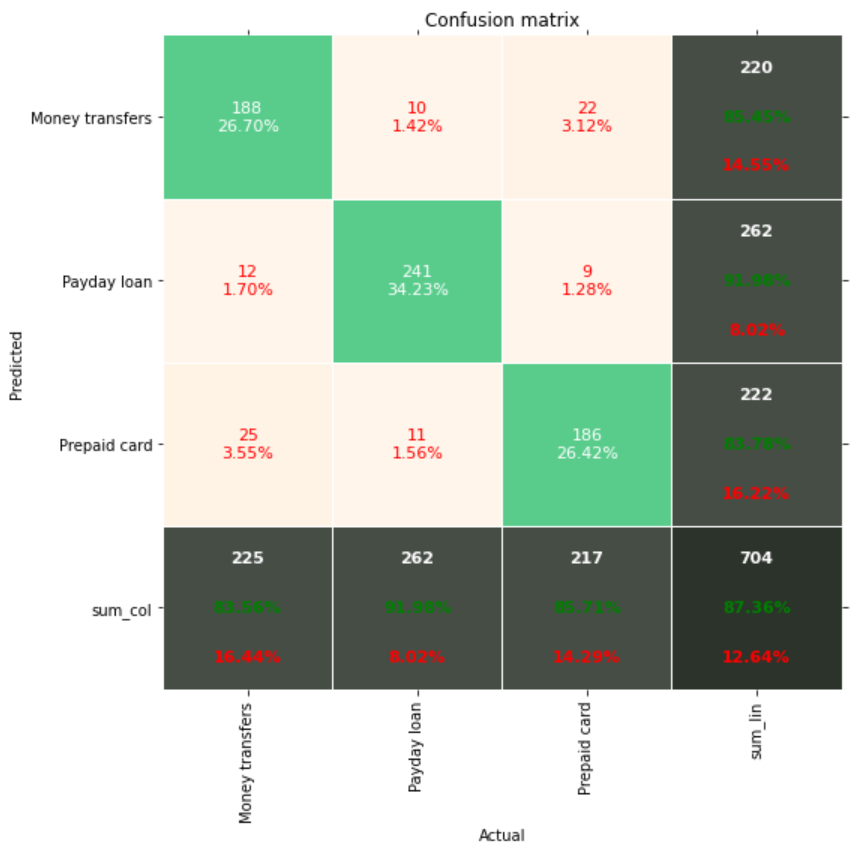
BERT
BERT and other Transformer encoder architectures have proven to be quite effective in a range of NLP tasks (natural language processing). They create natural language vector-space representations that can be used in deep learning models. The Transformer encoder architecture is used by the BERT family of models to process each token of input text in the context of all tokens before and after it, hence the name: Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. Typically, BERT models are trained on a huge corpus of text before being fine-tuned for specific tasks.
class BERTBaseUncased(MultiClass):
def __init__(self, num_classes, learning_rate=3e-5):
super(BERTBaseUncased, self).__init__()
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.3)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(768, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
outputs = self.bert(x)
b_o = self.dropout(outputs.pooler_output)
logits = self.classifier(b_o)
return logits
def freeze_bert_encoder(self):
for param in self.bert.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
def unfreeze_bert_encoder(self):
for param in self.bert.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
def configure_optimizers(self):
optimizer = AdamW(self.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate)
return optimizerStart training.
bert = BERTBaseUncased(3)
bert.unfreeze_bert_encoder()
trainer = pl.Trainer(gpus=1, fast_dev_run=False, max_epochs=40, precision=16, deterministic=True)
trainer.fit(bert, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader)
test_probs = bert.predict(test_dataloader)
test_preds = np.argmax(test_probs, axis=1)Visualise the accuracy and loss.
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(bert.train_accuracies)), bert.train_accuracies, label="train")
plt.plot(range(len(bert.valid_accuracies)), bert.valid_accuracies, label="valid")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()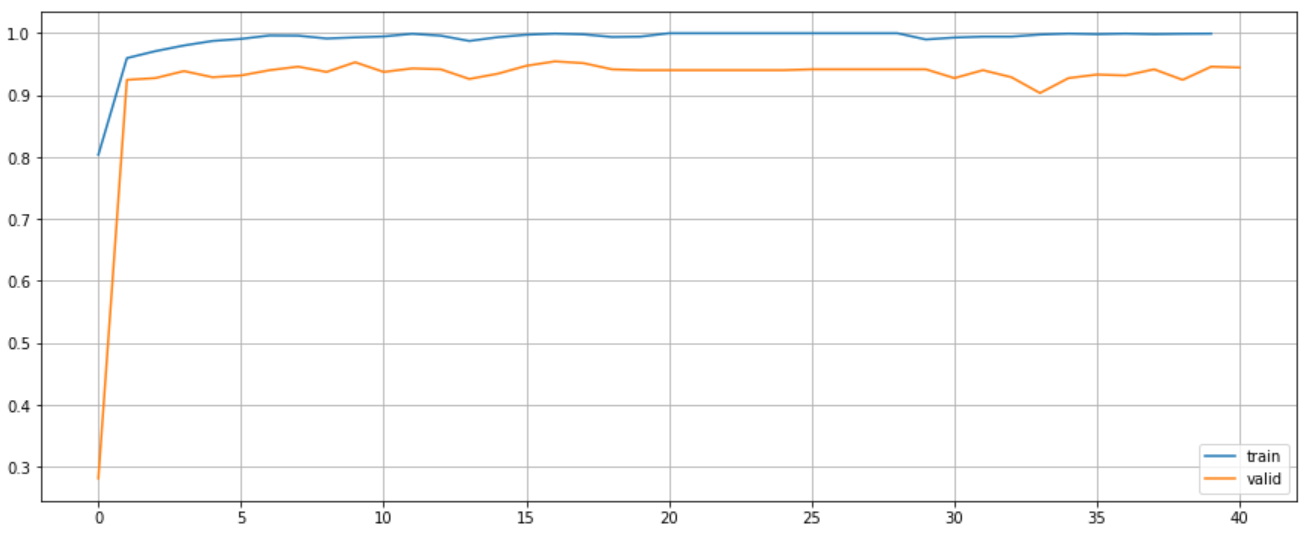
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(bert.train_losses)), bert.train_losses, label="train")
plt.plot(range(len(bert.valid_losses)), bert.valid_losses, label="valid")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()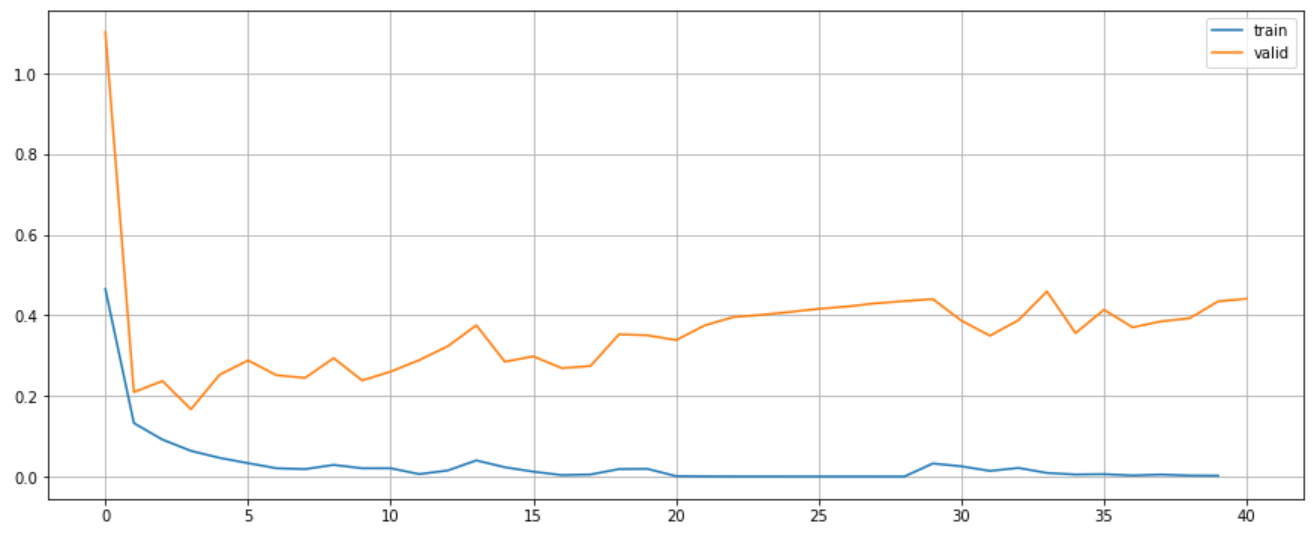
Confusion matrix.
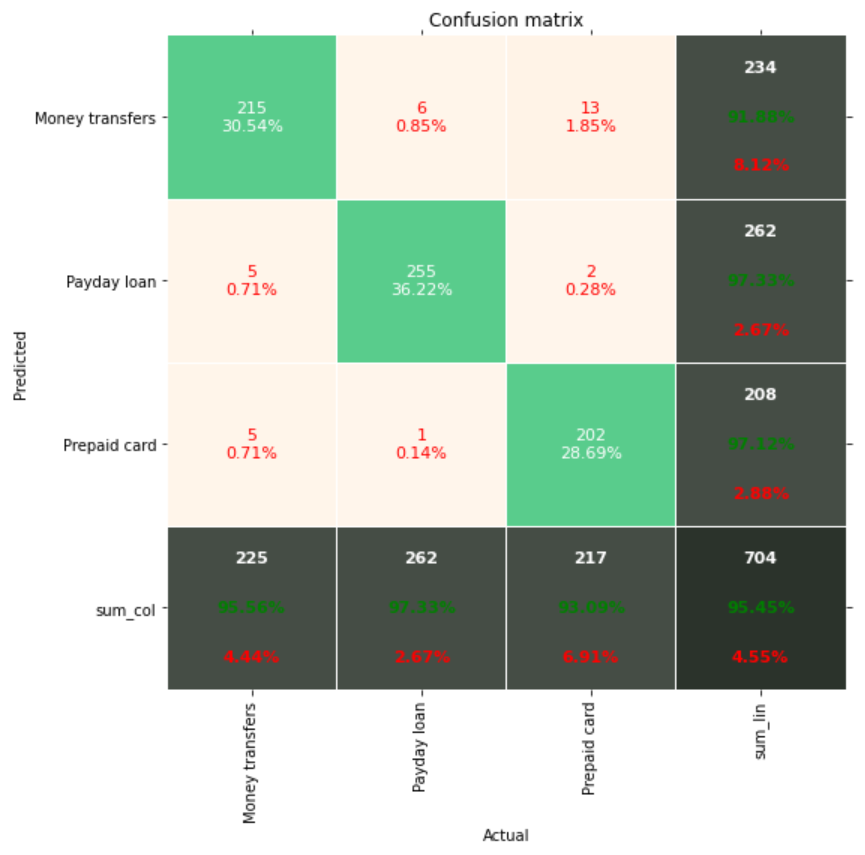
Performance
| Index | Model | Accuracy | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LSTM | 0.8736 | 0.8736 |
| 2 | TextCNN | 0.9284 | 0.9289 |
| 3 | XVectors | 0.7958 | 0.7898 |
| 4 | BERT | 0.9545 | 0.9545 |
Conclusion
You learned how to utilise BERT Tokenizer to produce word embeddings that can be used to do text categorisation in this post. On the test set, we achieved an accuracy of 95.45% using sentimental analysis of Consumer Complaint Database dataset.
References
- https://stackabuse.com/text-classification-with-bert-tokenizer-and-tf-2-0-in-python/
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2001.06397.pdf
- https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/587
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1408.5882.pdf
- https://www.ijcai.org/Proceedings/16/Papers/408.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805.pdf
- https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/tensorboard_tutorial.html
- https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/latest/common/trainer.html
- https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/latest/starter/introduction_guide.html
- https://github.com/PyTorchLightning/pytorch-lightning

